What is Powder Metallurgy?
- Top
- Business
- Powder Metallurgy
- What is Powder Metallurgy?
- What is Powder Metallurgy?
- Characteristics of Powder Metallurgy
- Powder Metallurgy Characteristics, Technologies, and Products
- Industries where Powder Metallurgy is Used
What is Powder Metallurgy?
Powder metallurgy is one kind of forging technology, in which powdered materials such as metals and ceramics are processed to make parts and other shapes.
After being filled in a “die” in the shape of a product and pressed in a press machine, powder takes the form of the product at the time when it is removed from the die. This reduces the amount of machining and other processing, which can result in significant cost reductions.

Multiple materials can be mixed, making it easy to select materials to meet customer needs.

Characteristics of Powder Metallurgy
High Performance
Various materials can be combined to achieve material properties with multiple functions. These include wear resistance, sliding properties, magnetism, high machinability, current collection properties, and heat resistance.
Lightweight
Weight reduction is possible by controlling the product density during powder compaction. (Approx. 85% of castings)
Resource Saving
Products are formed using a die that matches the shape of the product, eliminating the need for machining in the profile direction. This results in a reduction in scrap materials.
High Quality
High dimensional accuracy of less than 1/100 mm in product dimensions is ensured by our high dimensional accuracy die design and compaction technologies. Our integrated production process ensures stable product quality.

Energy Saving
General sintering temperature is 1,000°C to 1,300°C, which is lower than the melting temperature of castings, thus reducing energy consumption.

Environmental Friendliness
We manufacture products in consideration of carbon neutrality, contributing to resource saving, energy saving, weight reduction, and other energy consumption reductions.

Low Cost
Mass production on an integrated production line enables a reduction in costs. Furthermore, we contribute to a reduction in product costs by reducing machining processes using a die compaction process and by proposing Simultaneous Engineering (SE) for shape design.
Powder Metallurgy Products and Their Technologies and Methods
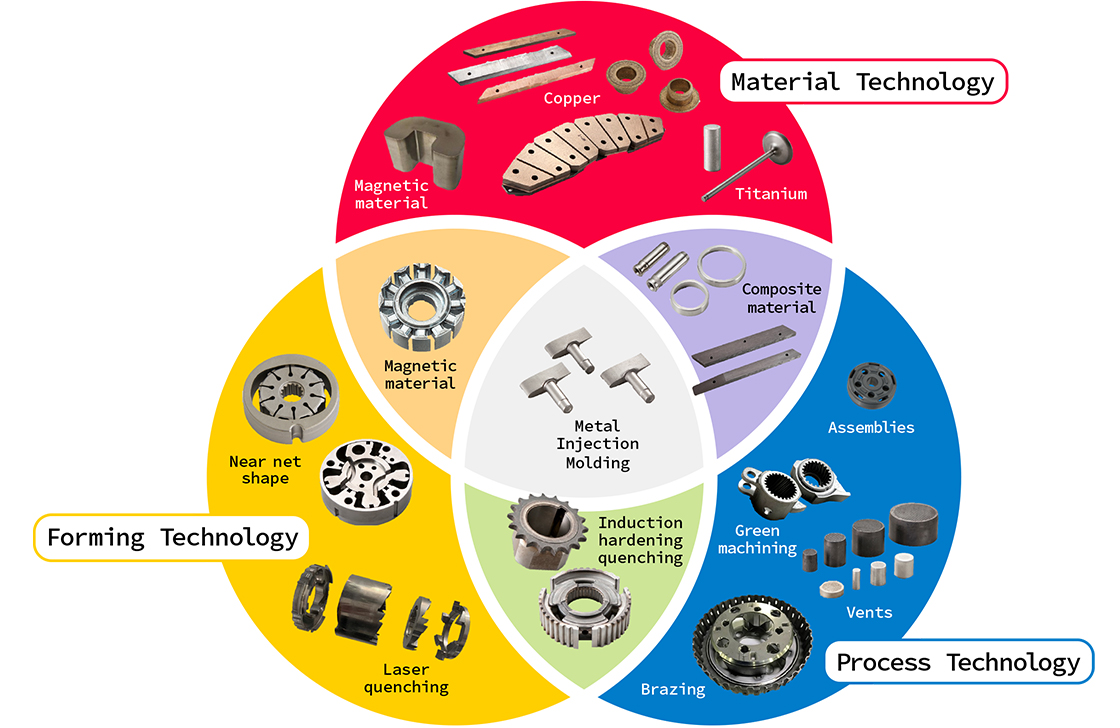
Main Industries where Powder Metallurgy is Used
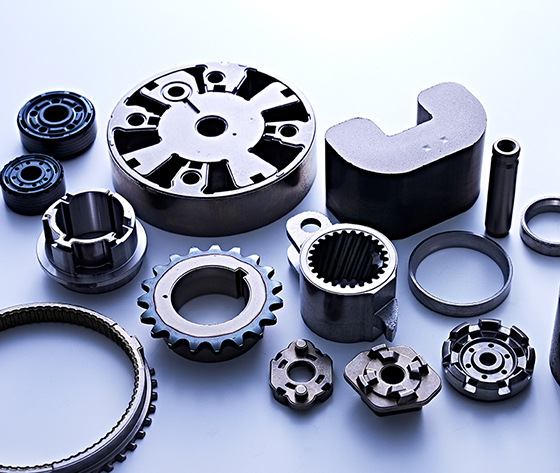

Automotive Parts
We manufacture a wide variety of parts for engines, shock absorbers, transmissions and steering systems. In particular, our products for shock absorbers are used in automobiles all over the world, dominating the global market for shock absorber parts. Even if the parts are used for the same location, such as the underbody, the shape, size, required strength, etc., will differ for light vehicles and heavy-duty trucks. Therefore, materials and production method must be decided according to the required specifications and target costs.
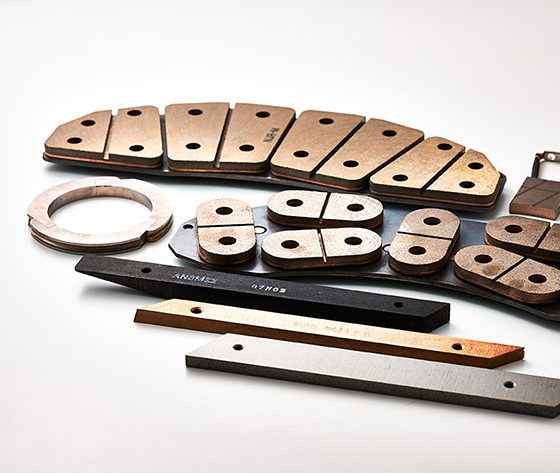

Parts for Railway Vehicles
We manufacture pantograph current collectors used in electric trains to obtain electricity from the overhead wires and the brake linings used to stop Shinkansen bullet trains. As a characteristic, the pantograph current collectors efficiently draw electricity from the overhead wires without damaging the wires, and the brake linings can withstand temperatures of 1,000°C or higher and still maintain friction as a brake. These products take advantage of material characteristics that would be difficult to achieve without using powder metallurgy, and have been adopted by JR (Japan Railway) and private railway companies based on our accumulated achievements.
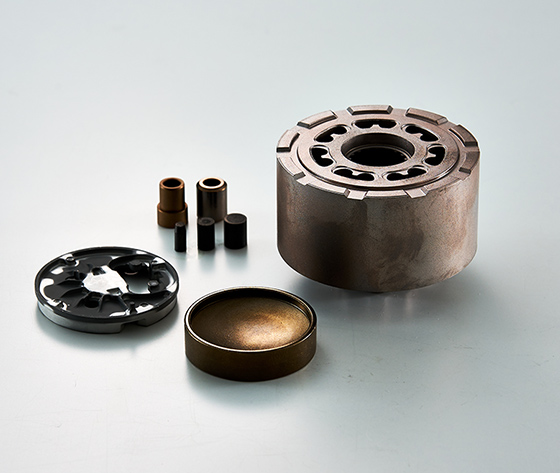


Parts for Industrial Machinery
We manufacture parts for industrial machinery across a wide range of industries, from construction machinery to copiers, cameras, electric tools, and more. We use powder metallurgy to manufacture net-shape parts of complex shapes, and manufacture products that meet our customer needs and contribute to lower costs by taking advantage of the characteristics of materials such as iron, copper, stainless steel and aluminum.